- HOME
-
PRODUCTS


-
ELECTRICAL PROBE SYSTEMS
- ANALYTICAL PROBE STATIONS
- BENCHTOP PROBE STATIONS
- STANDARD MINI PROBE STAGES
- SPECIALTY MINI PROBE STAGES
- WAFER CHUCKS
-
THERMAL PLATES
- BENCHTOP THERMAL PLATES
- COMPACT THERMAL PLATES
- SPECIALTY THERMAL PLATES
- HALL EFFECT MEASURMENT
- ELECTRONICS PRODUCTS
- CONTROLLERS, COOLING SYSTEMS AND ACCESSORIES
- OPTICAL EQUIPMENT
-
LIQUID CRYSTAL SYSTEMS
- ALCT SYSTEM
- LC SYSTEM ACCESSORIES
- LC MATERIALS
- CUSTOM PRODUCTS
RESOURCES ![]()
![]()
SUPPORT ![]()
![]()
ABOUT ![]()
![]()
STATIC OPERATION
• In normal operation the controller uses a PID algorithm to adjust heating power and cooling pumping flow to maintain the current temperature
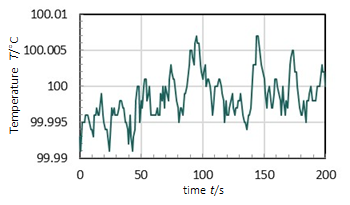
RAMP OPERATION
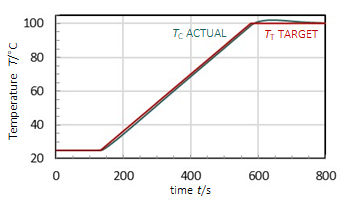
• To ramp to a user-defined target temperature TT at a specified ramp rate R from a current temperature TC, the controller calculates a target temperature profile
• The controller then adjusts the heating power and cooling pumping flow to achieve the target temperature profile
• In a real system, the wiring, a sample on the heating block, and the surrounding atmosphere are thermal loads that dissipate power
• Electrical and thermal inertia can result in short time delays in electrical and thermal responses and in achieving stability in the target temperature
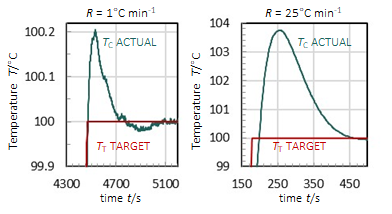
• Faster ramp rates can result in greater overshooting of target temperatures because of thermal inertia
• Overshoot and delay can never be eliminated fully in a real system, but can be minimized by using the slowest ramp rate possible for the process
SAMPLE COOLING
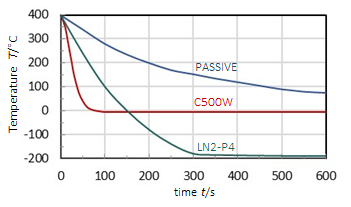
• To achieve below ambient temperatures an active cooling system is necessary: a recirculating water chiller or a liquid nitrogen cooling system
• Active cooling has the advantage over passive cooling to allow fast experiment cycling
FRAME COOLING SYSTEMS
• Frame cooling option with recirculating chiller allows thermal control of frame independent of sample thermal block
• Keeps frame safe to touch and prevents frost buildup on windows
LIQUID NITROGEN COOLING SYSTEMS
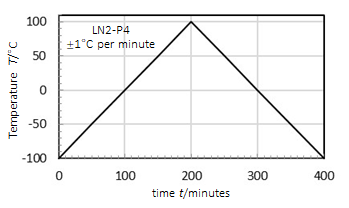
• Liquid nitrogen systems provide sample cooling to as low as -190°C depending on pump power and thermal block size
• Systems consist of a pump, a Dewar, a lid with a stoppered port for refilling during operation, and connecting tubing
• Three liquid nitrogen pump output options available, LN2-P2, LN2-P4, and LN2-P8, which suction liquid nitrogen through the equipment and are controlled by the mK2000
• Three Dewar sizes, 2 L, 10 L, and 30 L, with easy refillable lid options to control liquid nitrogen supply to instruments
• Integrates with mK2000 PID controller with ±0.1% resolution
LIQUID NITROGEN SYSTEM MINIMUM TEMPERATURES | |||
LN2-P2 |
LN2-P4 |
LN2-P8 |
|
STAGES | |||
HCS302/302G/402 |
-100°C |
-190°C |
-190°C |
HCS321Gi |
-60°C |
-70°C |
-80°C |
HCS621G/421V |
-160°C |
-190°C |
-190°C |
HCS622G/422V |
-100°C |
-190°C |
-190°C |
FS1 |
NA |
-60°C |
-190°C |
CLM77K/CLM77Ki |
NA |
-190°C |
-190°C |
CHUCKS & PLATES | |||
100mm square or round |
-40°C |
-60°C |
-120°C |
150mm square or round |
-20°C |
-40°C |
-100°C |
200mm square or round |
NA |
-30°C |
-80°C |
300mm square or round |
NA |
-20°C |
-60°C |
HCC602 |
-120°C |
-170°C |
-190°C |
