- HOME
-
PRODUCTS


-
ELECTRICAL PROBE SYSTEMS
- ANALYTICAL PROBE STATIONS
- BENCHTOP PROBE STATIONS
- STANDARD MINI PROBE STAGES
- SPECIALTY MINI PROBE STAGES
- WAFER CHUCKS
-
THERMAL PLATES
- BENCHTOP THERMAL PLATES
- COMPACT THERMAL PLATES
- SPECIALTY THERMAL PLATES
- HALL EFFECT MEASURMENT
- ELECTRONICS PRODUCTS
- CONTROLLERS, COOLING SYSTEMS AND ACCESSORIES
- OPTICAL EQUIPMENT
-
LIQUID CRYSTAL SYSTEMS
- ALCT SYSTEM
- LC SYSTEM ACCESSORIES
- LC MATERIALS
- CUSTOM PRODUCTS
RESOURCES ![]()
![]()
SUPPORT ![]()
![]()
ABOUT ![]()
![]()
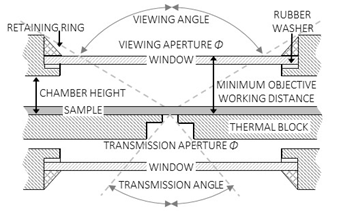
TOP & BOTTOM WINDOWS
• All stages feature a top aperture and many stages feature a transmission aperture and a bottom window
• The top viewing window consists of an opening in the top cover and the bottom window consists of an opening in the bottom frame
• Top and bottom windows are secured with a flat rubber O-ring on the interior side and a metal screwing retaining ring on the exterior side
• The top and bottom aperture magnitude is the effective diameter of the window, limited on the outer edge by the retaining ring and the rubber O-ring
• This aperture magnitude is typically 4 mm less than the window disc diameter
• Different window sizes are available as options.
• Removable and interchangeable windows accommodate the full spectrum of light sources and techniques
• Heat loss scales with window area. Windows are circular and sized according to application to balance maximum viewing angle and minimum heat loss
OPTICAL PATH
• The optical path on stages is through a top viewing window, a transmission aperture in the block, and a bottom window
• The top viewing angle is the maximum angle made from the edges of the window retaining ring and the center of the thermal block top surface
• The top viewing angle depends on the chamber height and the window diameter
• The top viewing angle is double the angle from normal
• The transmission aperture is the minimum diameter of the cylindrical hole through the heating block
• Standard transmission aperture is 2 mm diameter with options of 5 mm or 8 mm diameters
• The transmission angle is the maximum angle made from the edges of the transmission aperture and the center of the thermal block bottom surface
OBJECTIVE & CONDENSER
• The minimum objective working distance is the distance between the top surface of the thermal block and the outer surface of the viewing window
• Sample height reduces the minimum objective working distance
• If the actual objective working distance is less than the minimum working distance, a focused image is not achieved
• Removing the outer windows results in shorter working distances, but compromises sample thermal isolation and risks exposing the lenses to damaging heat
• The minimum condenser working distance is the distance between the bottom surface of the thermal block and the outer surface of the bottom window
• Longer working distance condensers are necessary to focus images through the thermal block using Kohler illumination in modern microscopes
INTEGRATED WINDOW DEFROST
• Some models feature top viewing window defrost mechanism for use with inert or dry gas supply
• One option is an integrated channel in the top cover with a hose port
• Another option is an externally mounted hose holder that allows easy positioning of the hose tip anywhere on the window
